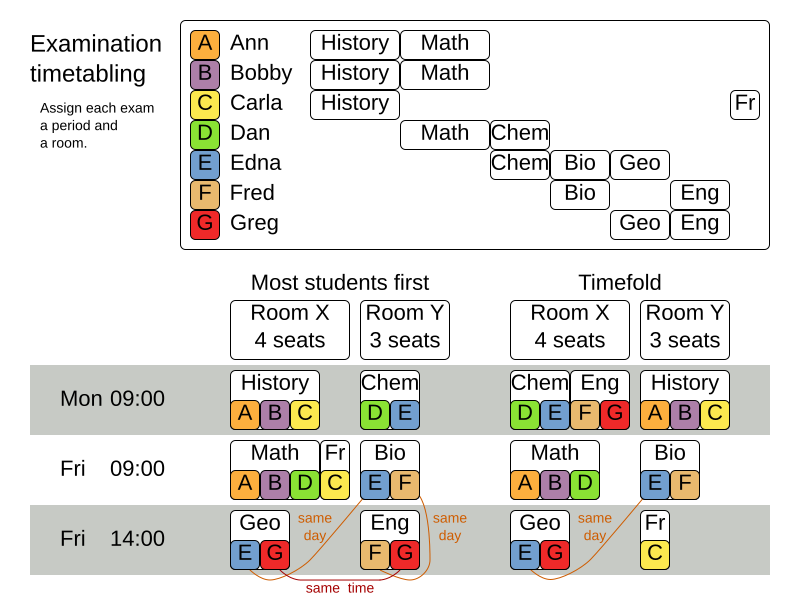
Exam timetabling (ITC 2007 track 1 - Examination)
Problem description
Schedule each exam into a period and into a room. Multiple exams can share the same room during the same period.
Hard constraints:
-
Exam conflict: two exams that share students must not occur in the same period.
-
Room capacity: A room’s seating capacity must suffice at all times.
-
Period duration: A period’s duration must suffice for all of its exams.
-
Period related hard constraints (specified per dataset):
-
Coincidence: two specified exams must use the same period (but possibly another room).
-
Exclusion: two specified exams must not use the same period.
-
After: A specified exam must occur in a period after another specified exam’s period.
-
-
Room related hard constraints (specified per dataset):
-
Exclusive: one specified exam should not have to share its room with any other exam.
-
Soft constraints (each of which has a parametrized penalty):
-
The same student should not have two exams in a row.
-
The same student should not have two exams on the same day.
-
Period spread: two exams that share students should be a number of periods apart.
-
Mixed durations: two exams that share a room should not have different durations.
-
Front load: Large exams should be scheduled earlier in the schedule.
-
Period penalty (specified per dataset): Some periods have a penalty when used.
-
Room penalty (specified per dataset): Some rooms have a penalty when used.
It uses large test data sets of real-life universities.
The problem is defined by the International Timetabling Competition 2007 track 1. Geoffrey De Smet finished 4th in that competition with a very early version of Timefold. Many improvements have been made since then.
Problem size
exam_comp_set1 has 7883 students, 607 exams, 54 periods, 7 rooms, 12 period constraints and 0 room constraints with a search space of 10^1564.
exam_comp_set2 has 12484 students, 870 exams, 40 periods, 49 rooms, 12 period constraints and 2 room constraints with a search space of 10^2864.
exam_comp_set3 has 16365 students, 934 exams, 36 periods, 48 rooms, 168 period constraints and 15 room constraints with a search space of 10^3023.
exam_comp_set4 has 4421 students, 273 exams, 21 periods, 1 rooms, 40 period constraints and 0 room constraints with a search space of 10^360.
exam_comp_set5 has 8719 students, 1018 exams, 42 periods, 3 rooms, 27 period constraints and 0 room constraints with a search space of 10^2138.
exam_comp_set6 has 7909 students, 242 exams, 16 periods, 8 rooms, 22 period constraints and 0 room constraints with a search space of 10^509.
exam_comp_set7 has 13795 students, 1096 exams, 80 periods, 15 rooms, 28 period constraints and 0 room constraints with a search space of 10^3374.
exam_comp_set8 has 7718 students, 598 exams, 80 periods, 8 rooms, 20 period constraints and 1 room constraints with a search space of 10^1678.Domain model
Below you can see the main examination domain classes:
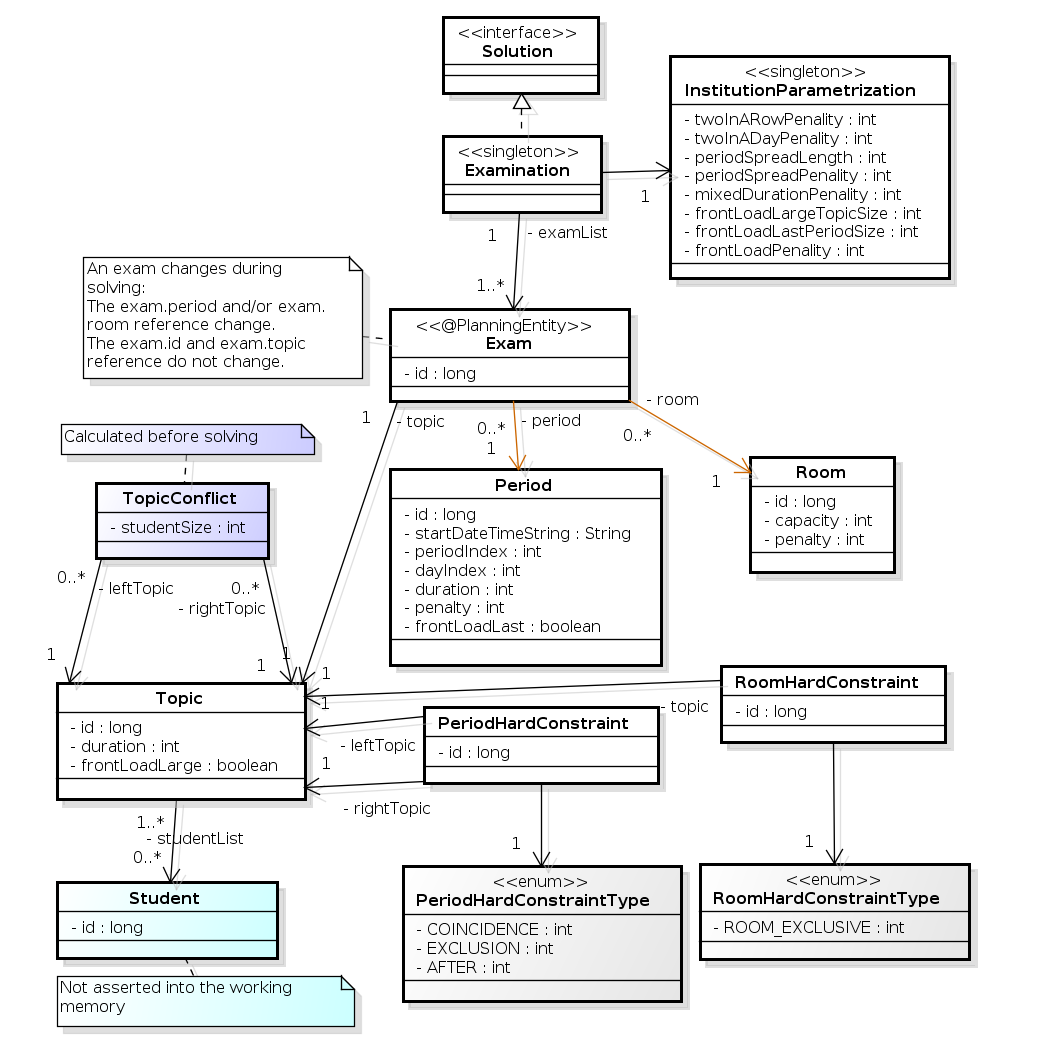
Notice that we’ve split up the exam concept into an Exam class and a Topic class.
The Exam instances change during solving (this is the planning entity class), when their period or room property changes.
The Topic, Period and Room instances never change during solving (these are problem facts, just like some other classes).