Vehicle Routing Quick Start Guide
1. What you will build
You will build a REST application that optimizes a Vehicle Route Problem (VRP):
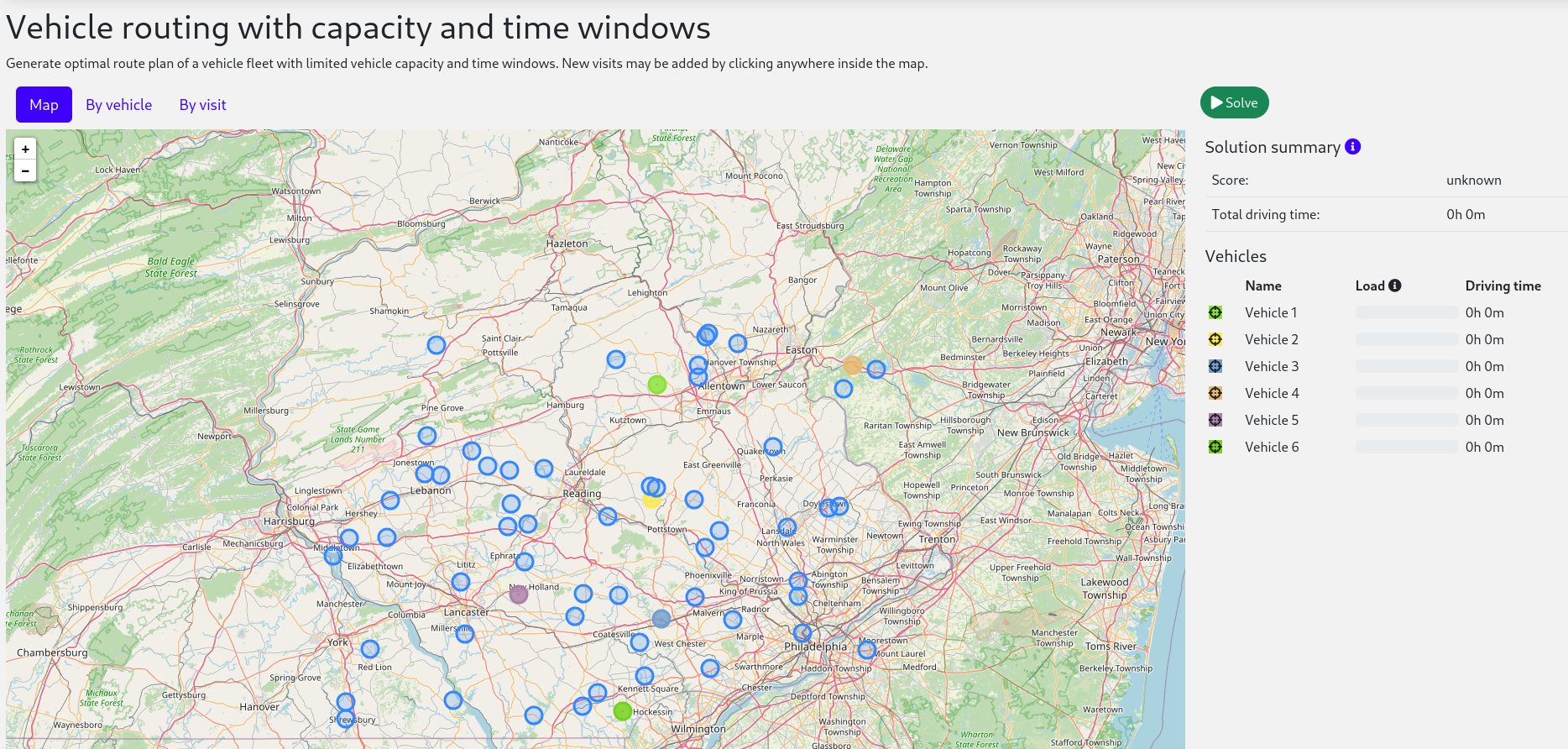
Your service will assign Visit instances to Vehicle instances automatically
by using AI to adhere to hard and soft scheduling constraints, such as the following examples:
-
The demand for a vehicle cannot exceed its capacity.
-
The deliveries have specific deadlines that must be met.
-
The less total travel time, the better.
Mathematically speaking, VRP is an NP-hard problem. This means it is difficult to scale. Simply brute force iterating through all possible combinations takes millions of years for a non-trivial dataset, even on a supercomputer. Luckily, AI constraint solvers such as Timefold Solver have advanced algorithms that deliver a near-optimal solution in a reasonable amount of time.
2. Solution source code
Follow the instructions in the next sections to create the application step by step (recommended).
Alternatively, you can also skip right to the completed example:
-
Clone the Git repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/TimefoldAI/timefold-quickstartsor download an archive.
-
Find the solution in the
javadirectory and run it (see its README file).
3. Prerequisites
To complete this guide, you need:
-
JDK 17+ with
JAVA_HOMEconfigured appropriately. For example with Sdkman:$ curl -s "https://get.sdkman.io" | bash $ sdk install java -
Apache Maven 3.9.11+ or Gradle 7+
-
An IDE, such as IntelliJ IDEA, VSCode or Eclipse
4. The build file and the dependencies
Use code.quarkus.io to generate an application with the following extensions, for Maven or Gradle:
|
Clicking the link above will automatically select the dependencies for you on code.quarkus.io. |
-
Quarkus REST JAX-RS (
quarkus-rest) -
Quarkus REST Jackson (
quarkus-rest-jackson) -
Timefold Solver (
timefold-solver-quarkus) -
Timefold Solver Jackson (
timefold-solver-quarkus-jackson)
Your pom.xml file has the following content:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.acme</groupId>
<artifactId>vehicle-routing</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.release>11</maven.compiler.release>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<version.io.quarkus>3.30.6</version.io.quarkus>
<version.ai.timefold.solver>1.30.0</version.ai.timefold.solver>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<!-- Alternatively, use <artifactId>quarkus-universe-bom</artifactId>
which includes both quarkus-bom and timefold-solver-bom. -->
<artifactId>quarkus-bom</artifactId>
<version>${version.io.quarkus}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-bom</artifactId>
<version>${version.ai.timefold.solver}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-rest-jackson</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-quarkus</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-quarkus-jackson</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${version.compiler.plugin}</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${version.io.quarkus}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>build</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<systemPropertyVariables>
<java.util.logging.manager>org.jboss.logmanager.LogManager</java.util.logging.manager>
</systemPropertyVariables>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.acme</groupId>
<artifactId>vehicle-routing</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.release>11</maven.compiler.release>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<version.io.quarkus>3.30.6</version.io.quarkus>
<version.ai.timefold.solver>1.30.0</version.ai.timefold.solver>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<!-- Alternatively, use <artifactId>quarkus-universe-bom</artifactId>
which includes both quarkus-bom and timefold-solver-bom. -->
<artifactId>quarkus-bom</artifactId>
<version>${version.io.quarkus}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-bom</artifactId>
<version>${version.ai.timefold.solver}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-rest</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-rest-jackson</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-quarkus</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-quarkus-jackson</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>kotlin-stdlib</artifactId>
<version>1.9.22</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/kotlin</sourceDirectory>
<testSourceDirectory>src/test/kotlin</testSourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${version.compiler.plugin}</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${version.io.quarkus}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>build</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<systemPropertyVariables>
<java.util.logging.manager>org.jboss.logmanager.LogManager</java.util.logging.manager>
</systemPropertyVariables>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>kotlin-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${version.kotlin}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>compile</id>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>test-compile</id>
<goals>
<goal>test-compile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>kotlin-maven-allopen</artifactId>
<version>${version.kotlin}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<javaParameters>true</javaParameters>
<jvmTarget>17</jvmTarget>
<compilerPlugins>
<plugin>all-open</plugin>
</compilerPlugins>
<pluginOptions>
<option>all-open:annotation=jakarta.ws.rs.Path</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=jakarta.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=io.quarkus.test.junit.QuarkusTest</option>
</pluginOptions>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>5. Model the domain objects
Your goal is to assign each visit to a vehicle. You will create these classes:
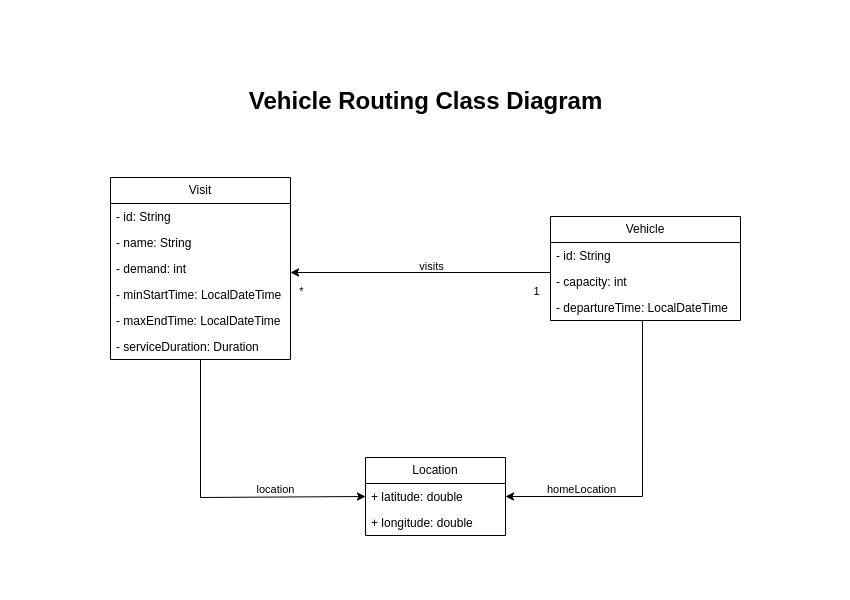
5.1. Location
The Location class is used to represent the destination for deliveries or the home location for vehicles.
The drivingTimeSeconds map contains the time required to drive from this location to any other location.
This field will be initialized later.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Location.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain;
import java.util.Map;
public class Location {
private double latitude;
private double longitude;
private Map<Location, Long> drivingTimeSeconds;
public Location(double latitude, double longitude) {
this.latitude = latitude;
this.longitude = longitude;
}
public double getLatitude() {
return latitude;
}
public double getLongitude() {
return longitude;
}
public Map<Location, Long> getDrivingTimeSeconds() {
return drivingTimeSeconds;
}
public void setDrivingTimeSeconds(Map<Location, Long> drivingTimeSeconds) {
this.drivingTimeSeconds = drivingTimeSeconds;
}
public long getDrivingTimeTo(Location location) {
return drivingTimeSeconds.get(location);
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Location.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain
class Location @JsonCreator constructor(val latitude: Double, val longitude: Double) {
var drivingTimeSeconds: Map<Location, Long>? = null
fun getDrivingTimeTo(location: Location): Long {
if (drivingTimeSeconds == null) {
return 0
}
return drivingTimeSeconds!![location]!!
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "$latitude,$longitude"
}
}5.2. Vehicle
Vehicle has a defined route plan with scheduled visits to make.
Each vehicle has a specific departure time and starting location.
It returns to its home location after completing the route and has a maximum capacity that must not be exceeded.
During solving, Timefold Solver updates the visits field of the Vehicle class to assign a list of visits.
Because Timefold Solver changes this field, Vehicle is a planning entity:
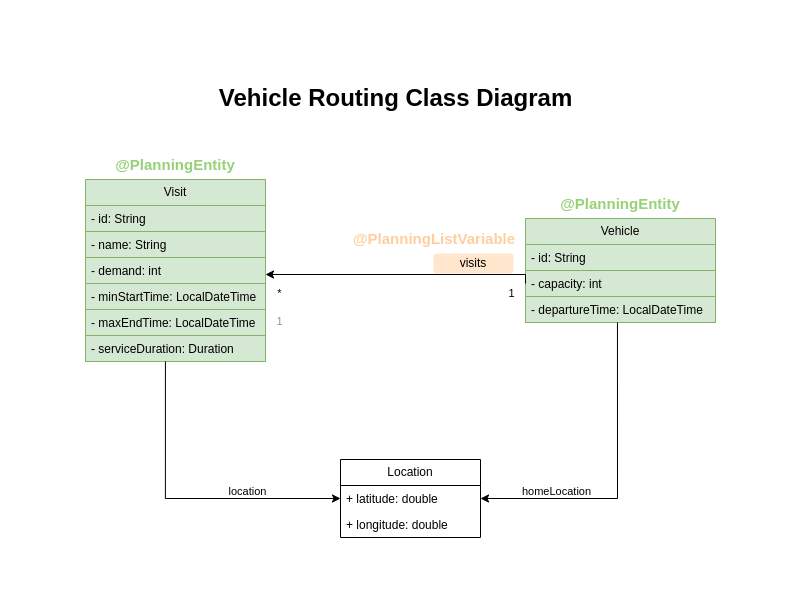
Based on the diagram, the visits field is a genuine variable that changes during the solving process.
To ensure that Timefold Solver recognizes it as a sequence of connected variables,
the field must have an @PlanningListVariable annotation indicating that the solver can distribute a subset of the
available visits to it.
The objective is to create an ordered scheduled visit plan for each vehicle.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Vehicle.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.entity.PlanningEntity;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.lookup.PlanningId;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.PlanningListVariable;
@PlanningEntity
public class Vehicle {
@PlanningId
private String id;
private int capacity;
private Location homeLocation;
private LocalDateTime departureTime;
@PlanningListVariable
private List<Visit> visits;
public Vehicle() {
}
public Vehicle(String id, int capacity, Location homeLocation, LocalDateTime departureTime) {
this.id = id;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.homeLocation = homeLocation;
this.departureTime = departureTime;
this.visits = new ArrayList<>();
}
// Getters and Setters excluded
public int getTotalDemand() {
int totalDemand = 0;
for (Visit visit : visits) {
totalDemand += visit.getDemand();
}
return totalDemand;
}
public long getTotalDrivingTimeSeconds() {
if (visits.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
long totalDrivingTime = 0;
Location previousLocation = homeLocation;
for (Visit visit : visits) {
totalDrivingTime += previousLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(visit.getLocation());
previousLocation = visit.getLocation();
}
totalDrivingTime += previousLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(homeLocation);
return totalDrivingTime;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id;
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Vehicle.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain
import java.time.LocalDateTime
import java.util.ArrayList
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.entity.PlanningEntity
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.lookup.PlanningId
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.PlanningListVariable
@PlanningEntity
class Vehicle {
@PlanningId
lateinit var id: String
var capacity: Int = 0
lateinit var homeLocation: Location
lateinit var departureTime: LocalDateTime
@PlanningListVariable
var visits: List<Visit>? = null
constructor()
constructor(id: String, capacity: Int, homeLocation: Location, departureTime: LocalDateTime) {
this.id = id
this.capacity = capacity
this.homeLocation = homeLocation
this.departureTime = departureTime
this.visits = ArrayList()
}
val totalDemand: Long
get() {
var totalDemand = 0L
for (visit in visits!!) {
totalDemand += visit.demand
}
return totalDemand
}
val totalDrivingTimeSeconds: Long
get() {
if (visits!!.isEmpty()) {
return 0
}
var totalDrivingTime: Long = 0
var previousLocation = homeLocation
for (visit in visits!!) {
totalDrivingTime += previousLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(visit.location!!)
previousLocation = visit.location!!
}
totalDrivingTime += previousLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(homeLocation)
return totalDrivingTime
}
override fun toString(): String {
return id
}
}The Vehicle class has an @PlanningEntity annotation,
so Timefold Solver knows that this class changes during solving because it contains one or more planning variables.
Notice the toString() method keeps the output short,
so it is easier to read Timefold Solver’s DEBUG or TRACE log, as shown later.
|
Determining the |
5.3. Visit
The Visit class represents a delivery that needs to be made by vehicles.
A visit includes a destination location, a delivery time window represented by [minStartTime, maxEndTime],
a demand that needs to be fulfilled by the vehicle, and a service duration time.
The Visit class has an @PlanningEntity annotation
but no genuine variables and is called a shadow entity.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create or adjust the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Visit.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.entity.PlanningEntity;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.lookup.PlanningId;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.InverseRelationShadowVariable;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.NextElementShadowVariable;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.PreviousElementShadowVariable;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.ShadowVariable;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.solver.ArrivalTimeUpdatingVariableListener;
@PlanningEntity
public class Visit {
@PlanningId
private String id;
private String name;
private Location location;
private int demand;
private LocalDateTime minStartTime;
private LocalDateTime maxEndTime;
private Duration serviceDuration;
@InverseRelationShadowVariable(sourceVariableName = "visits")
private Vehicle vehicle;
@PreviousElementShadowVariable(sourceVariableName = "visits")
private Visit previousVisit;
@CascadingUpdateShadowVariable(targetMethodName = "updateArrivalTime")
private LocalDateTime arrivalTime;
public Visit() {
}
public Visit(String id, String name, Location location, int demand,
LocalDateTime minStartTime, LocalDateTime maxEndTime, Duration serviceDuration) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.location = location;
this.demand = demand;
this.minStartTime = minStartTime;
this.maxEndTime = maxEndTime;
this.serviceDuration = serviceDuration;
}
// Getters and Setters excluded
private void updateArrivalTime() {
if (previousVisit == null && vehicle == null) {
arrivalTime = null;
return;
}
LocalDateTime departureTime = previousVisit == null ? vehicle.getDepartureTime() : previousVisit.getDepartureTime();
arrivalTime = departureTime != null ? departureTime.plusSeconds(getDrivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill()) : null;
}
public LocalDateTime getDepartureTime() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return null;
}
return getStartServiceTime().plus(serviceDuration);
}
public LocalDateTime getStartServiceTime() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return null;
}
return arrivalTime.isBefore(minStartTime) ? minStartTime : arrivalTime;
}
public boolean isServiceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime() {
return arrivalTime != null
&& arrivalTime.plus(serviceDuration).isAfter(maxEndTime);
}
public long getServiceFinishedDelayInMinutes() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return 0;
}
return Duration.between(maxEndTime, arrivalTime.plus(serviceDuration)).toMinutes();
}
public long getDrivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill() {
if (vehicle == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"This method must not be called when the shadow variables are not initialized yet.");
}
if (previousVisit == null) {
return vehicle.getHomeLocation().getDrivingTimeTo(location);
}
return previousVisit.getLocation().getDrivingTimeTo(location);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id;
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Visit.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain
import java.time.Duration
import java.time.LocalDateTime
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.entity.PlanningEntity
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.lookup.PlanningId
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.InverseRelationShadowVariable
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.NextElementShadowVariable
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.PreviousElementShadowVariable
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.ShadowVariable
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.solver.ArrivalTimeUpdatingVariableListener
@PlanningEntity
class Visit {
@PlanningId
lateinit var id: String
lateinit var name: String
lateinit var location: Location
var demand: Int = 0
lateinit var minStartTime: LocalDateTime
lateinit var maxEndTime: LocalDateTime
lateinit var serviceDuration: Duration
@InverseRelationShadowVariable(sourceVariableName = "visits")
private var vehicle: Vehicle? = null
@PreviousElementShadowVariable(sourceVariableName = "visits")
var previousVisit: Visit? = null
@CascadingUpdateShadowVariable(targetMethodName = "updateArrivalTime")
var arrivalTime: LocalDateTime? = null
constructor()
constructor(
id: String, name: String, location: Location, demand: Int,
minStartTime: LocalDateTime, maxEndTime: LocalDateTime, serviceDuration: Duration
) {
this.id = id
this.name = name
this.location = location
this.demand = demand
this.minStartTime = minStartTime
this.maxEndTime = maxEndTime
this.serviceDuration = serviceDuration
}
private fun updateArrivalTime() {
if (previousVisit == null && vehicle == null) {
arrivalTime = null
return
}
val departureTime = previousVisit?.departureTime ?: vehicle?.departureTime
arrivalTime = departureTime?.plusSeconds(getDrivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill())
}
val departureTime: LocalDateTime?
get() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return null
}
return startServiceTime!!.plus(serviceDuration)
}
val startServiceTime: LocalDateTime?
get() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return null
}
return if (arrivalTime!!.isBefore(minStartTime)) minStartTime else arrivalTime
}
val isServiceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime: Boolean
get() = (arrivalTime != null
&& arrivalTime!!.plus(serviceDuration).isAfter(maxEndTime))
val serviceFinishedDelayInMinutes: Long
get() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return 0
}
return Duration.between(maxEndTime, arrivalTime!!.plus(serviceDuration)).toMinutes()
}
val drivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill: Long
get() {
if (vehicle == null) {
throw IllegalStateException(
"This method must not be called when the shadow variables are not initialized yet."
)
}
if (previousVisit == null) {
return vehicle!!.homeLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(location)
}
return previousVisit!!.location.getDrivingTimeTo((location))
}
override fun toString(): String {
return id
}
}Some methods are annotated with @InverseRelationShadowVariable, @PreviousElementShadowVariable and @CascadingUpdateShadowVariable.
They are called shadow variables,
and because Timefold Solver changes them,
Visit is a planning entity:
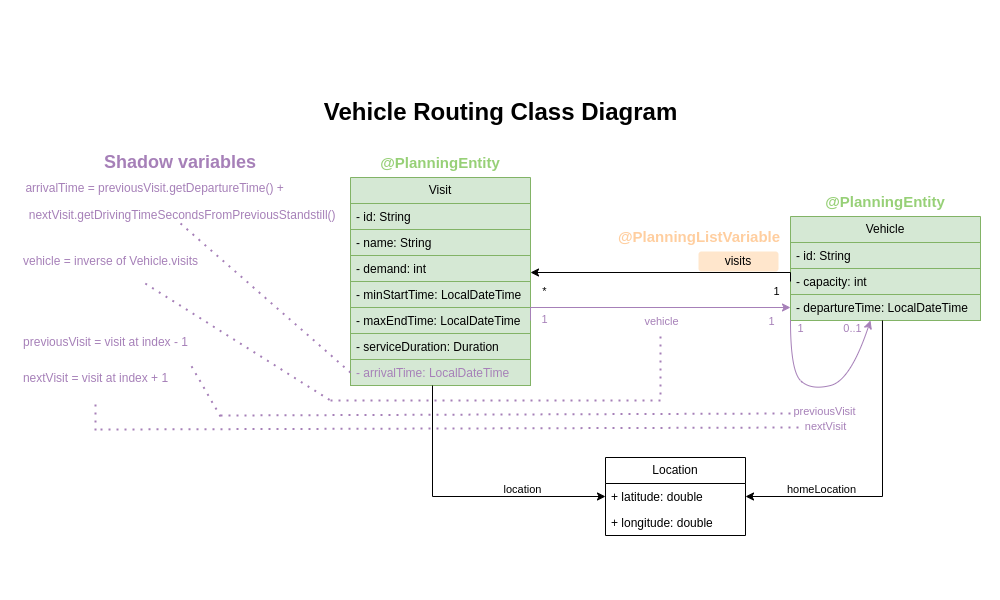
The field vehicle has an @InverseRelationShadowVariable annotation,
creating a bi-directional relationship with the Vehicle.
The function returns a reference to the Vehicle where the visit is scheduled.
Let’s say the visit Ann was scheduled to the vehicle V1 during the solving process.
The method returns a reference of V1.
The field previousVisit is annotated with @PreviousElementShadowVariable.
The solver will update this field with a reference of the visit preceding the current visit instance.
Assuming that vehicle V1 is assigned the visits of Ann, Beth, and Carl,
the previousVisit field will be filled with Ann for the visit of Beth.
@NextElementShadowVariable also exists, which can be used to get a reference to the successor element.
|
The arrivalTime field has a @CascadingUpdateShadowVariable annotation.
This annotation indicates which method should be triggered to update this field whenever this entity is moved, in this case the updateArrivalTime() method.
This change is automatically propagated to the subsequent visits and stops when the arrivalTime value hasn’t changed or when it’s reached the end of the chain of visit objects.
6. Define the constraints and calculate the score
A score represents the quality of a specific solution. The higher the better. Timefold Solver looks for the best solution, which is the solution with the highest score found in the available time. It might be the optimal solution.
Because this use case has hard and soft constraints,
use the HardSoftScore class to represent the score:
-
Hard constraints must not be broken. For example: The vehicle capacity must not be exceeded.
-
Soft constraints should not be broken. For example: The sum total of travel time.
Hard constraints are weighted against other hard constraints. Soft constraints are weighted too, against other soft constraints. Hard constraints always outweigh soft constraints, regardless of their respective weights.
To calculate the score, create a VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider class
to perform incremental score calculation.
It uses Timefold Solver’s Constraint Streams API
which is inspired by Java Streams and SQL:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create a src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/solver/VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.solver;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.buildin.hardsoftlong.HardSoftLongScore;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.Constraint;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.ConstraintFactory;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.ConstraintProvider;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Visit;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Vehicle;
public class VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider implements ConstraintProvider {
public static final String VEHICLE_CAPACITY = "vehicleCapacity";
public static final String SERVICE_FINISHED_AFTER_MAX_END_TIME = "serviceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime";
public static final String MINIMIZE_TRAVEL_TIME = "minimizeTravelTime";
@Override
public Constraint[] defineConstraints(ConstraintFactory factory) {
return new Constraint[] {
vehicleCapacity(factory),
serviceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime(factory),
minimizeTravelTime(factory)
};
}
protected Constraint vehicleCapacity(ConstraintFactory factory) {
return factory.forEach(Vehicle.class)
.filter(vehicle -> vehicle.getTotalDemand() > vehicle.getCapacity())
.penalizeLong(HardSoftLongScore.ONE_HARD,
vehicle -> vehicle.getTotalDemand() - vehicle.getCapacity())
.asConstraint(VEHICLE_CAPACITY);
}
protected Constraint serviceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime(ConstraintFactory factory) {
return factory.forEach(Visit.class)
.filter(Visit::isServiceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime)
.penalizeLong(HardSoftLongScore.ONE_HARD,
Visit::getServiceFinishedDelayInMinutes)
.asConstraint(SERVICE_FINISHED_AFTER_MAX_END_TIME);
}
protected Constraint minimizeTravelTime(ConstraintFactory factory) {
return factory.forEach(Vehicle.class)
.penalizeLong(HardSoftLongScore.ONE_SOFT,
Vehicle::getTotalDrivingTimeSeconds)
.asConstraint(MINIMIZE_TRAVEL_TIME);
}
}Create a src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/solver/VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.solver
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.buildin.hardsoftlong.HardSoftLongScore
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.Constraint
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.ConstraintFactory
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.ConstraintProvider
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Visit
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Vehicle
class VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider : ConstraintProvider {
override fun defineConstraints(factory: ConstraintFactory): Array<Constraint> {
return arrayOf(
vehicleCapacity(factory),
serviceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime(factory),
minimizeTravelTime(factory)
)
}
protected fun vehicleCapacity(factory: ConstraintFactory): Constraint {
return factory.forEach(Vehicle::class.java)
.filter({ vehicle: Vehicle -> vehicle.totalDemand > vehicle.capacity })
.penalizeLong(
HardSoftLongScore.ONE_HARD
) { vehicle: Vehicle -> vehicle.totalDemand - vehicle.capacity }
.asConstraint(VEHICLE_CAPACITY)
}
protected fun serviceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime(factory: ConstraintFactory): Constraint {
return factory.forEach(Visit::class.java)
.filter({ obj: Visit -> obj.isServiceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime })
.penalizeLong(HardSoftLongScore.ONE_HARD,
{ obj: Visit -> obj.serviceFinishedDelayInMinutes })
.asConstraint(SERVICE_FINISHED_AFTER_MAX_END_TIME)
}
protected fun minimizeTravelTime(factory: ConstraintFactory): Constraint {
return factory.forEach(Vehicle::class.java)
.penalizeLong(HardSoftLongScore.ONE_SOFT,
{ obj: Vehicle -> obj.totalDrivingTimeSeconds })
.asConstraint(MINIMIZE_TRAVEL_TIME)
}
companion object {
const val VEHICLE_CAPACITY: String = "vehicleCapacity"
const val SERVICE_FINISHED_AFTER_MAX_END_TIME: String = "serviceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime"
const val MINIMIZE_TRAVEL_TIME: String = "minimizeTravelTime"
}
}7. Gather the domain objects in a planning solution
A VehicleRoutePlan wraps all Vehicle and Visit instances of a single dataset.
Furthermore, because it contains all vehicles and visits, each with a specific planning variable state,
it is a planning solution
and it has a score:
-
If visits are still unassigned, then it is an uninitialized solution.
-
If it breaks hard constraints, then it is an infeasible solution, for example, a solution with the score
-2hard/-3soft. -
If it adheres to all hard constraints, then it is a feasible solution, for example, a solution with the score
0hard/-7soft.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/VehicleRoutePlan.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningEntityCollectionProperty;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningScore;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningSolution;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.valuerange.ValueRangeProvider;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.buildin.hardsoftlong.HardSoftLongScore;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.solver.SolverStatus;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo.DrivingTimeCalculator;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo.HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator;
@PlanningSolution
public class VehicleRoutePlan {
@PlanningEntityCollectionProperty
private List<Vehicle> vehicles;
@PlanningEntityCollectionProperty
@ValueRangeProvider
private List<Visit> visits;
@PlanningScore
private HardSoftLongScore score;
// Fields and constructors used for visualization excluded
public VehicleRoutePlan() {
}
public VehicleRoutePlan(String name,
List<Vehicle> vehicles,
List<Visit> visits) {
this.name = name;
this.vehicles = vehicles;
this.visits = visits;
// Enhance locations with a pre-calculated driving time map
List<Location> locations = Stream.concat(
vehicles.stream().map(Vehicle::getHomeLocation),
visits.stream().map(Visit::getLocation)).toList();
DrivingTimeCalculator drivingTimeCalculator = HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator.getInstance();
drivingTimeCalculator.initDrivingTimeMaps(locations);
}
// Getters and Setters excluded
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/VehicleRoutePlan.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain;
import java.time.LocalDateTime
import java.util.stream.Stream
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningEntityCollectionProperty
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningScore
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningSolution
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.valuerange.ValueRangeProvider
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.buildin.hardsoftlong.HardSoftLongScore
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.solver.SolverStatus
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo.DrivingTimeCalculator
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo.HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator
@PlanningSolution
class VehicleRoutePlan {
lateinit var name: String
@PlanningEntityCollectionProperty
var vehicles: List<Vehicle>? = null
private set
@PlanningEntityCollectionProperty
@ValueRangeProvider
var visits: List<Visit>? = null
private set
@PlanningScore
var score: HardSoftLongScore? = null
// Fields and constructors used for visualization excluded
constructor()
constructor(
name: String,
vehicles: List<Vehicle>,
visits: List<Visit>
) {
this.name = name
this.vehicles = vehicles
this.visits = visits
// Enhance locations with a pre-calculated driving time map
val locations = Stream.concat(
vehicles.stream().map({ obj: Vehicle -> obj.homeLocation }),
visits.stream().map({ obj: Visit -> obj.location })
).toList()
val drivingTimeCalculator: DrivingTimeCalculator = HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator.INSTANCE
drivingTimeCalculator.initDrivingTimeMaps(locations)
}
}The VehicleRoutePlan class has an @PlanningSolution annotation,
so Timefold Solver knows that this class contains all of the input and output data.
Specifically, these classes are the input of the problem:
-
The
vehiclesfield with all vehicles-
This is a list of planning entities, because they change during solving.
-
For each
Vehicle:-
The value of the
visitsis typically stillempty, so unassigned. It is a planning variable. -
The other fields, such as
capacity,homeLocationanddepartureTime, are filled in. These fields are problem properties.
-
-
-
The
visitsfield with all visits-
This is a list of planning entities, because they change during solving.
-
For each
Visit:-
The values of
vehicle,previousVisit,nextVisit,arrivalTimeare typically stillnullfor a fresh solution. They are planning shadow variables. -
The other fields, such as
name,locationanddemand, are filled in. These fields are problem properties.
-
-
However, this class is also the output of the solution:
-
The
vehiclesfield for which eachVehicleinstance has non-nullvisitsfield after solving. -
The
scorefield that represents the quality of the output solution, for example,0hard/-5soft.
7.1. The value range providers
The visits field is a value range provider.
It holds the Visit instances which Timefold Solver can pick from to assign to the visits field of Vehicle instances.
The visits field has an @ValueRangeProvider annotation to connect the @PlanningListVariable with the @ValueRangeProvider,
by matching the type of the planning list variable with the type returned by the value range provider.
7.2. Distance calculation
A matrix of distances between each location is typically calculated before starting the solver. First create a contract for driving time calculation:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/geo/DrivingTimeCalculator.java interface:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Location;
public interface DrivingTimeCalculator {
long calculateDrivingTime(Location from, Location to);
default Map<Location, Map<Location, Long>> calculateBulkDrivingTime(
Collection<Location> fromLocations,
Collection<Location> toLocations) {
return fromLocations.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(
Function.identity(),
from -> toLocations.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(
Function.identity(),
to -> calculateDrivingTime(from, to)))));
}
default void initDrivingTimeMaps(Collection<Location> locations) {
Map<Location, Map<Location, Long>> drivingTimeMatrix = calculateBulkDrivingTime(locations, locations);
locations.forEach(location -> location.setDrivingTimeSeconds(drivingTimeMatrix.get(location)));
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/geo/DrivingTimeCalculator.kt interface:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Location
import java.util.function.Function
import java.util.stream.Collectors
interface DrivingTimeCalculator {
fun calculateDrivingTime(from: Location, to: Location): Long
fun calculateBulkDrivingTime(
fromLocations: Collection<Location>,
toLocations: Collection<Location>
): Map<Location, Map<Location, Long>> {
return fromLocations.stream().collect(
Collectors.toMap(
Function.identity()
) { from: Location ->
toLocations.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.toMap(
Function.identity(),
{ to: Location ->
calculateDrivingTime(
from,
to
)
})
)
}
)
}
fun initDrivingTimeMaps(locations: Collection<Location>) {
val drivingTimeMatrix = calculateBulkDrivingTime(locations, locations)
locations.forEach { location: Location ->
location.drivingTimeSeconds = drivingTimeMatrix[location]
}
}
}Then create an implementation using Haversine method:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/geo/HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Location;
public final class HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator implements DrivingTimeCalculator {
private static final HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator INSTANCE = new HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator();
public static final int AVERAGE_SPEED_KMPH = 50;
private static final int EARTH_RADIUS_IN_M = 6371000;
private static final int TWICE_EARTH_RADIUS_IN_M = 2 * EARTH_RADIUS_IN_M;
static long metersToDrivingSeconds(long meters) {
return Math.round((double) meters / AVERAGE_SPEED_KMPH * 3.6);
}
public static synchronized HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
private HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator() {
}
@Override
public long calculateDrivingTime(Location from, Location to) {
if (from.equals(to)) {
return 0L;
}
CartesianCoordinate fromCartesian = locationToCartesian(from);
CartesianCoordinate toCartesian = locationToCartesian(to);
return metersToDrivingSeconds(calculateDistance(fromCartesian, toCartesian));
}
private long calculateDistance(CartesianCoordinate from, CartesianCoordinate to) {
if (from.equals(to)) {
return 0L;
}
double dX = from.x - to.x;
double dY = from.y - to.y;
double dZ = from.z - to.z;
double r = Math.sqrt((dX * dX) + (dY * dY) + (dZ * dZ));
return Math.round(TWICE_EARTH_RADIUS_IN_M * Math.asin(r));
}
private CartesianCoordinate locationToCartesian(Location location) {
double latitudeInRads = Math.toRadians(location.getLatitude());
double longitudeInRads = Math.toRadians(location.getLongitude());
// Cartesian coordinates, normalized for a sphere of diameter 1.0
double cartesianX = 0.5 * Math.cos(latitudeInRads) * Math.sin(longitudeInRads);
double cartesianY = 0.5 * Math.cos(latitudeInRads) * Math.cos(longitudeInRads);
double cartesianZ = 0.5 * Math.sin(latitudeInRads);
return new CartesianCoordinate(cartesianX, cartesianY, cartesianZ);
}
private record CartesianCoordinate(double x, double y, double z) {
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/geo/HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo
import kotlin.math.asin
import kotlin.math.sqrt
import kotlin.math.cos
import kotlin.math.sin
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Location
class HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator private constructor() : DrivingTimeCalculator {
override fun calculateDrivingTime(from: Location, to: Location): Long {
if (from == to) {
return 0L
}
val fromCartesian = locationToCartesian(from)
val toCartesian = locationToCartesian(to)
return metersToDrivingSeconds(calculateDistance(fromCartesian, toCartesian))
}
private fun calculateDistance(from: CartesianCoordinate, to: CartesianCoordinate): Long {
if (from == to) {
return 0L
}
val dX = from.x - to.x
val dY = from.y - to.y
val dZ = from.z - to.z
val r: Double = sqrt((dX * dX) + (dY * dY) + (dZ * dZ))
return Math.round(TWICE_EARTH_RADIUS_IN_M * asin(r))
}
private fun locationToCartesian(location: Location): CartesianCoordinate {
val latitudeInRads = Math.toRadians(location.latitude)
val longitudeInRads = Math.toRadians(location.longitude)
// Cartesian coordinates, normalized for a sphere of diameter 1.0
val cartesianX: Double = 0.5 * cos(latitudeInRads) * sin(longitudeInRads)
val cartesianY: Double = 0.5 * cos(latitudeInRads) * cos(longitudeInRads)
val cartesianZ: Double = 0.5 * sin(latitudeInRads)
return CartesianCoordinate(cartesianX, cartesianY, cartesianZ)
}
private data class CartesianCoordinate(val x: Double, val y: Double, val z: Double)
companion object {
@JvmStatic
@get:Synchronized
val INSTANCE: HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator = HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator()
const val AVERAGE_SPEED_KMPH: Int = 50
private const val EARTH_RADIUS_IN_M = 6371000
private const val TWICE_EARTH_RADIUS_IN_M = 2 * EARTH_RADIUS_IN_M
fun metersToDrivingSeconds(meters: Long): Long {
return Math.round(meters.toDouble() / AVERAGE_SPEED_KMPH * 3.6)
}
}
}8. Create the solver service
Now you are ready to put everything together and create a REST service.
But solving planning problems on REST threads causes HTTP timeout issues.
Therefore, the Quarkus extension injects a SolverManager instance,
which runs solvers in a separate thread pool
and can solve multiple datasets in parallel.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/rest/VehicleRoutePlanResource.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.rest;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
import jakarta.ws.rs.Consumes;
import jakarta.ws.rs.POST;
import jakarta.ws.rs.Path;
import jakarta.ws.rs.Produces;
import jakarta.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.solver.SolverJob;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.solver.SolverManager;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.VehicleRoutePlan;
@Path("route-plans")
public class VehicleRoutePlanResource {
private final SolverManager<VehicleRoutePlan, String> solverManager;
public VehicleRoutePlanResource() {
this.solverManager = null;
}
@Inject
public VehicleRoutePlanResource(SolverManager<VehicleRoutePlan, String> solverManager) {
this.solverManager = solverManager;
}
@POST
@Consumes({ MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON })
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public VehicleRoutePlan solve(VehicleRoutePlan problem) {
String jobId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
SolverJob<VehicleRoutePlan, String> solverJob = solverManager.solveBuilder()
.withProblemId(jobId)
.withProblem(problem)
.run();
VehicleRoutePlan solution;
try {
// Wait until the solving ends
solution = solverJob.getFinalBestSolution();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Solving failed.", e);
}
return solution;
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/rest/VehicleRoutePlanResource.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.rest
import java.util.UUID
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException
import jakarta.inject.Inject
import jakarta.ws.rs.Consumes
import jakarta.ws.rs.POST
import jakarta.ws.rs.Path
import jakarta.ws.rs.Produces
import jakarta.ws.rs.core.MediaType
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.solver.SolverManager
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.VehicleRoutePlan
@Path("route-plans")
class VehicleRoutePlanResource {
private val solverManager: SolverManager<VehicleRoutePlan, String>?
constructor() {
this.solverManager = null
}
@Inject
constructor(solverManager: SolverManager<VehicleRoutePlan, String>?) {
this.solverManager = solverManager
}
@POST
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
fun solve(problem: VehicleRoutePlan): VehicleRoutePlan {
val jobId = UUID.randomUUID().toString()
val solverJob = solverManager!!.solveBuilder()
.withProblemId(jobId)
.withProblem(problem)
.run()
val solution: VehicleRoutePlan
try {
// Wait until the solving ends
solution = solverJob.finalBestSolution
} catch (e: InterruptedException) {
throw IllegalStateException("Solving failed.", e)
} catch (e: ExecutionException) {
throw IllegalStateException("Solving failed.", e)
}
return solution
}
}For simplicity’s sake, this initial implementation waits for the solver to finish, which can still cause an HTTP timeout. The complete implementation avoids HTTP timeouts much more elegantly.
9. Set the termination time
Without a termination setting or a terminationEarly() event, the solver runs forever.
To avoid that, limit the solving time to five seconds.
That is short enough to avoid the HTTP timeout.
Create the src/main/resources/application.properties file:
# The solver runs only for 5 seconds to avoid a HTTP timeout in this simple implementation.
# It's recommended to run for at least 5 minutes ("5m") otherwise.
quarkus.timefold.solver.termination.spent-limit=5sTimefold Solver returns the best solution found in the available termination time. Due to the nature of NP-hard problems, the best solution might not be optimal, especially for larger datasets. Increase the termination time to potentially find a better solution.
10. Run the application
First start the application:
$ mvn compile quarkus:dev10.1. Try the application
Now that the application is running, you can test the REST service.
You can use any REST client you wish.
The following example uses the Linux command curl to send a POST request:
$ curl -i -X POST http://localhost:8080/route-plans -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{"name":"demo","vehicles":[{"id":"1","capacity":15,"homeLocation":[40.605994321126936,-75.68106859680056],"departureTime":"2024-02-10T07:30:00"},{"id":"2","capacity":25,"homeLocation":[40.32196770776356,-75.69785667307953],"departureTime":"2024-02-10T07:30:00"}],"visits":[{"id":"1","name":"Dan Green","location":[40.76104493121754,-75.16056341466826],"demand":1,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T13:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T18:00:00","serviceDuration":1200},{"id":"2","name":"Ivy King","location":[40.13754381024318,-75.492526629236],"demand":1,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T13:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T18:00:00","serviceDuration":1200.000000000},{"id":"3","name":"Flo Li","location":[39.87122455090297,-75.64520072015769],"demand":2,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T08:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T12:00:00","serviceDuration":600.000000000},{"id":"4","name":"Flo Cole","location":[40.46124744193433,-75.18250987609025],"demand":1,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T13:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T18:00:00","serviceDuration":2400.000000000},{"id":"5","name":"Carl Green","location":[40.61352381171549,-75.83301278355529],"demand":1,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T08:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T12:00:00","serviceDuration":1800.000000000}]}'After about five seconds, according to the termination spent time defined in your application.properties,
the service returns an output similar to the following example:
HTTP/1.1 200
Content-Type: application/json
...
{"name":"demo","vehicles":[{"id":"1","capacity":15,"homeLocation":[40.605994321126936,-75.68106859680056],"departureTime":"2024-02-10T07:30:00","visits":[<LIST OF VISITS ASSIGNED TO CAR 1>],"arrivalTime":"2024-02-10T15:34:11","totalDemand":3,"totalDrivingTimeSeconds":10826},{"id":"2","capacity":25,"homeLocation":[40.32196770776356,-75.69785667307953],"departureTime":"2024-02-10T07:30:00","visits":[<LIST OF VISITS ASSIGNED TO CAR 2>],"arrivalTime":"2024-02-10T13:52:18","totalDemand":3,"totalDrivingTimeSeconds":7890}],"visits":[{"id":"1","name":"Dan Green","location":[40.76104493121754,-75.16056341466826],"demand":1,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T13:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T18:00:00","serviceDuration":1200.000000000,"vehicle":"1","previousVisit":"5","nextVisit":"4","arrivalTime":"2024-02-10T09:40:50","startServiceTime":"2024-02-10T13:00:00","departureTime":"2024-02-10T13:20:00","drivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill":4250},{"id":"2","name":"Ivy King","location":[40.13754381024318,-75.492526629236],"demand":1,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T13:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T18:00:00","serviceDuration":1200.000000000,"vehicle":"2","previousVisit":"3","nextVisit":null,"arrivalTime":"2024-02-10T09:19:12","startServiceTime":"2024-02-10T13:00:00","departureTime":"2024-02-10T13:20:00","drivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill":2329},{"id":"3","name":"Flo Li","location":[39.87122455090297,-75.64520072015769],"demand":2,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T08:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T12:00:00","serviceDuration":600.000000000,"vehicle":"2","previousVisit":null,"nextVisit":"2","arrivalTime":"2024-02-10T08:30:23","startServiceTime":"2024-02-10T08:30:23","departureTime":"2024-02-10T08:40:23","drivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill":3623},{"id":"4","name":"Flo Cole","location":[40.46124744193433,-75.18250987609025],"demand":1,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T13:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T18:00:00","serviceDuration":2400.000000000,"vehicle":"1","previousVisit":"1","nextVisit":null,"arrivalTime":"2024-02-10T14:00:04","startServiceTime":"2024-02-10T14:00:04","departureTime":"2024-02-10T14:40:04","drivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill":2404},{"id":"5","name":"Carl Green","location":[40.61352381171549,-75.83301278355529],"demand":1,"minStartTime":"2024-02-10T08:00:00","maxEndTime":"2024-02-10T12:00:00","serviceDuration":1800.000000000,"vehicle":"1","previousVisit":null,"nextVisit":"1","arrivalTime":"2024-02-10T07:45:25","startServiceTime":"2024-02-10T08:00:00","departureTime":"2024-02-10T08:30:00","drivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill":925}],"score":"0hard/-18716soft","totalDrivingTimeSeconds":18716}Notice that your application assigned all five visits to one of the two vehicles.
Also notice that it conforms to all hard constraints.
For example, visits 1, 4, and 5 were scheduled to the vehicle 1.
On the server side, the info log shows what Timefold Solver did in those five seconds:
... Solving started: time spent (17), best score (0hard/0soft), environment mode (PHASE_ASSERT), move thread count (NONE), random (JDK with seed 0).
... Construction Heuristic phase (0) ended: time spent (33), best score (0hard/-18755soft), move evaluation speed (2222/sec), step total (5).
... Local Search phase (1) ended: time spent (5000), best score (0hard/-18716soft), move evaluation speed (89685/sec), step total (40343).
... Solving ended: time spent (5000), best score (0hard/-18716soft), move evaluation speed (89079/sec), phase total (2), environment mode (PHASE_ASSERT), move thread count (NONE).10.2. Test the application
A good application includes test coverage.
10.2.1. Test the constraints
To test each constraint in isolation, use a ConstraintVerifier in unit tests.
It tests each constraint’s corner cases in isolation from the other tests,
which lowers maintenance when adding a new constraint with proper test coverage.
First update your build tool configuration:
Add a timefold-solver-test dependency in your pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.quarkus</groupId>
<artifactId>quarkus-junit5</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>Then create the test itself:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/test/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/solver/VehicleRoutingConstraintProviderTest.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.solver;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.Arrays;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
import ai.timefold.solver.test.api.score.stream.ConstraintVerifier;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Location;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Vehicle;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.VehicleRoutePlan;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Visit;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo.HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import io.quarkus.test.junit.QuarkusTest;
@QuarkusTest
class VehicleRoutingConstraintProviderTest {
/*
* LOCATION_1 to LOCATION_2 is approx. 11713 m ~843 seconds of driving time
* LOCATION_2 to LOCATION_3 is approx. 8880 m ~639 seconds of driving time
* LOCATION_1 to LOCATION_3 is approx. 13075 m ~941 seconds of driving time
*/
private static final Location LOCATION_1 = new Location(49.288087, 16.562172);
private static final Location LOCATION_2 = new Location(49.190922, 16.624466);
private static final Location LOCATION_3 = new Location(49.1767533245638, 16.50422914190477);
private static final LocalDate TOMORROW = LocalDate.now().plusDays(1);
@Inject
ConstraintVerifier<VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider, VehicleRoutePlan> constraintVerifier;
@BeforeAll
static void initDrivingTimeMaps() {
HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator.getInstance().initDrivingTimeMaps(Arrays.asList(LOCATION_1, LOCATION_2, LOCATION_3));
}
@Test
void vehicleCapacityPenalized() {
LocalDateTime tomorrow_07_00 = LocalDateTime.of(TOMORROW, LocalTime.of(7, 0));
LocalDateTime tomorrow_08_00 = LocalDateTime.of(TOMORROW, LocalTime.of(8, 0));
LocalDateTime tomorrow_10_00 = LocalDateTime.of(TOMORROW, LocalTime.of(10, 0));
Vehicle vehicleA = new Vehicle("1", 100, LOCATION_1, tomorrow_07_00);
Visit visit1 = new Visit("2", "John", LOCATION_2, 80, tomorrow_08_00, tomorrow_10_00, Duration.ofMinutes(30L));
vehicleA.getVisits().add(visit1);
Visit visit2 = new Visit("3", "Paul", LOCATION_3, 40, tomorrow_08_00, tomorrow_10_00, Duration.ofMinutes(30L));
vehicleA.getVisits().add(visit2);
constraintVerifier.verifyThat(VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider::vehicleCapacity)
.given(vehicleA, visit1, visit2)
.penalizesBy(20);
}
}Create the src/test/kotlin/org/acme/schooltimetabling/solver/TimetableConstraintProviderTest.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.solver;
import java.time.Duration
import java.time.LocalDate
import java.time.LocalDateTime
import java.time.LocalTime
import java.util.Arrays
import jakarta.inject.Inject
import ai.timefold.solver.test.api.score.stream.ConstraintVerifier
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.ConstraintFactory
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Location
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Vehicle
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.VehicleRoutePlan
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.Visit
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.geo.HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
import io.quarkus.test.junit.QuarkusTest
@QuarkusTest
internal class VehicleRoutingConstraintProviderTest {
@Inject
lateinit var constraintVerifier: ConstraintVerifier<VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider, VehicleRoutePlan>
@Test
fun vehicleCapacityPenalized() {
val tomorrow_07_00 = LocalDateTime.of(TOMORROW, LocalTime.of(7, 0))
val tomorrow_08_00 = LocalDateTime.of(TOMORROW, LocalTime.of(8, 0))
val tomorrow_10_00 = LocalDateTime.of(TOMORROW, LocalTime.of(10, 0))
val vehicleA = Vehicle("1", 100, LOCATION_1, tomorrow_07_00)
val visit1 = Visit("2", "John", LOCATION_2, 80, tomorrow_08_00, tomorrow_10_00, Duration.ofMinutes(30L))
vehicleA.visits!!.add(visit1)
val visit2 = Visit("3", "Paul", LOCATION_3, 40, tomorrow_08_00, tomorrow_10_00, Duration.ofMinutes(30L))
vehicleA.visits!!.add(visit2)
constraintVerifier!!.verifyThat { obj: VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider, factory: ConstraintFactory? ->
obj.vehicleCapacity(
factory!!
)
}
.given(vehicleA, visit1, visit2)
.penalizesBy(20)
}
companion object {
/*
* LOCATION_1 to LOCATION_2 is approx. 11713 m ~843 seconds of driving time
* LOCATION_2 to LOCATION_3 is approx. 8880 m ~639 seconds of driving time
* LOCATION_1 to LOCATION_3 is approx. 13075 m ~941 seconds of driving time
*/
private val LOCATION_1 = Location(49.288087, 16.562172)
private val LOCATION_2 = Location(49.190922, 16.624466)
private val LOCATION_3 = Location(49.1767533245638, 16.50422914190477)
private val TOMORROW: LocalDate = LocalDate.now().plusDays(1)
@JvmStatic
@BeforeAll
fun initDrivingTimeMaps() {
HaversineDrivingTimeCalculator.INSTANCE.initDrivingTimeMaps(
Arrays.asList(
LOCATION_1, LOCATION_2, LOCATION_3
)
)
}
}
}This test verifies that the constraint VehicleRoutingConstraintProvider::vehicleCapacity,
when given two visits assigned to the same vehicle, penalizes with a match weight of 20 (exceeded capacity).
So with a constraint weight of 20hard it would reduce the score by -20hard.
Notice how ConstraintVerifier ignores the constraint weight during testing - even
if those constraint weights are hard coded in the ConstraintProvider - because
constraints weights change regularly before going into production.
This way, constraint weight tweaking does not break the unit tests.
10.2.2. Test the solver
In a JUnit test, generate a test dataset and send it to the VehicleRoutePlanResource to solve.
Add some dependencies in your pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured</groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.awaitility</groupId>
<artifactId>awaitility</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>Then create the test itself:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/test/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/rest/VehicleRoutePlanResourceTest.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.rest;
import static io.restassured.RestAssured.get;
import static io.restassured.RestAssured.given;
import static org.awaitility.Awaitility.await;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertNotNull;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.time.Duration;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.solver.SolverStatus;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.VehicleRoutePlan;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import io.quarkus.test.junit.QuarkusTest;
import io.restassured.http.ContentType;
@QuarkusTest
public class VehicleRoutePlanResourceTest {
@Test
public void solveDemoDataUntilFeasible() {
VehicleRoutePlan vehicleRoutePlan = given()
.when().get("/demo-data/FIRENZE")
.then()
.statusCode(200)
.extract()
.as(VehicleRoutePlan.class);
String jobId = given()
.contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.body(vehicleRoutePlan)
.expect().contentType(ContentType.TEXT)
.when().post("/route-plans")
.then()
.statusCode(200)
.extract()
.asString();
await()
.atMost(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.pollInterval(Duration.ofMillis(500L))
.until(() -> SolverStatus.NOT_SOLVING.name().equals(
get("/route-plans/" + jobId + "/status")
.jsonPath().get("solverStatus")));
VehicleRoutePlan solution = get("/route-plans/" + jobId).then().extract().as(VehicleRoutePlan.class);
assertEquals(solution.getSolverStatus(), SolverStatus.NOT_SOLVING);
assertNotNull(solution.getVehicles());
assertNotNull(solution.getVisits());
assertNotNull(solution.getVehicles().get(0).getVisits());
assertTrue(solution.getScore().isFeasible());
}
}Create the src/test/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/rest/VehicleRoutePlanResourceTest.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.rest
import java.time.Duration
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.solver.SolverStatus
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain.VehicleRoutePlan
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
import io.quarkus.test.junit.QuarkusTest
import io.restassured.RestAssured
import io.restassured.http.ContentType
import org.awaitility.Awaitility
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertNotNull
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue
@QuarkusTest
class VehicleRoutePlanResourceTest {
@Test
fun solveDemoDataUntilFeasible() {
val vehicleRoutePlan = RestAssured.given()
.`when`()["/demo-data/FIRENZE"]
.then()
.statusCode(200)
.extract()
.`as`(VehicleRoutePlan::class.java)
val jobId = RestAssured.given()
.contentType(ContentType.JSON)
.body(vehicleRoutePlan)
.expect().contentType(ContentType.TEXT)
.`when`().post("/route-plans")
.then()
.statusCode(200)
.extract()
.asString()
Awaitility.await()
.atMost(Duration.ofMinutes(1))
.pollInterval(Duration.ofMillis(500L))
.until {
SolverStatus.NOT_SOLVING.name == RestAssured.get("/route-plans/$jobId/status")
.jsonPath().get("solverStatus")
}
val solution = RestAssured.get("/route-plans/$jobId").then().extract().`as`(
VehicleRoutePlan::class.java
)
assertEquals(solution.solverStatus, SolverStatus.NOT_SOLVING)
assertNotNull(solution.vehicles)
assertNotNull(solution.visits)
assertNotNull(solution.vehicles!!.get(0).visits)
assertTrue(solution.score!!.isFeasible())
}
}This test verifies that after solving that it found a feasible solution (no hard constraints broken).
Add test properties to the src/main/resources/application.properties file:
quarkus.timefold.solver.termination.spent-limit=5s
# Effectively disable spent-time termination in favor of the best-score-limit
%test.quarkus.timefold.solver.termination.spent-limit=1h
%test.quarkus.timefold.solver.termination.best-score-limit=0hard/*softNormally, the solver finds a feasible solution in less than 200 milliseconds.
Notice how the application.properties overwrites the solver termination during tests
to terminate as soon as a feasible solution (0hard/*soft) is found.
This avoids hard coding a solver time, because the unit test might run on arbitrary hardware.
This approach ensures that the test runs long enough to find a feasible solution, even on slow machines.
But it does not run a millisecond longer than it strictly must, even on fast machines.
10.3. Logging
When adding constraints in your ConstraintProvider,
keep an eye on the move evaluation speed in the info log,
after solving for the same amount of time, to assess the performance impact:
... Solving ended: ..., move evaluation speed (29455/sec), ...To understand how Timefold Solver is solving your problem internally,
change the logging in the application.properties file or with a -D system property:
quarkus.log.category."ai.timefold.solver".level=debugUse debug logging to show every step:
... Solving started: time spent (67), best score (0hard/0soft), environment mode (PHASE_ASSERT), random (JDK with seed 0).
... CH step (0), time spent (128), score (0hard/0soft), selected move count (15), picked move ([Math(101) {null -> Room A}, Math(101) {null -> MONDAY 08:30}]).
... CH step (1), time spent (145), score (0hard/0soft), selected move count (15), picked move ([Physics(102) {null -> Room A}, Physics(102) {null -> MONDAY 09:30}]).
...Use trace logging to show every step and every move per step.
11. Summary
Congratulations! You have just developed a Quarkus application with Timefold!
For a full implementation with a web UI and in-memory storage, check out the Quarkus quickstart source code.