Introduction
1. What is Timefold Solver?
Every organization faces planning problems: providing products or services with a limited set of constrained resources (employees, assets, time and money). Timefold Solver optimizes such planning to do more business with less resources. This is known as Constraint Satisfaction Programming (which is part of the Operations Research discipline).
Timefold Solver is a lightweight, embeddable constraint satisfaction engine which optimizes planning problems. It solves use cases such as:
-
Employee shift rostering: timetabling nurses, repairmen, …
-
Agenda scheduling: scheduling meetings, appointments, maintenance jobs, advertisements, …
-
Educational timetabling: scheduling lessons, courses, exams, conference presentations, …
-
Vehicle routing: planning vehicle routes (trucks, trains, boats, airplanes, …) for moving freight and/or passengers through multiple destinations using known mapping tools …
-
Bin packing: filling containers, trucks, ships, and storage warehouses with items, but also packing information across computer resources, as in cloud computing …
-
Job shop scheduling: planning car assembly lines, machine queue planning, workforce task planning, …
-
Cutting stock: minimizing waste while cutting paper, steel, carpet, …
-
Sport scheduling: planning games and training schedules for football leagues, baseball leagues, …
-
Financial optimization: investment portfolio optimization, risk spreading, …
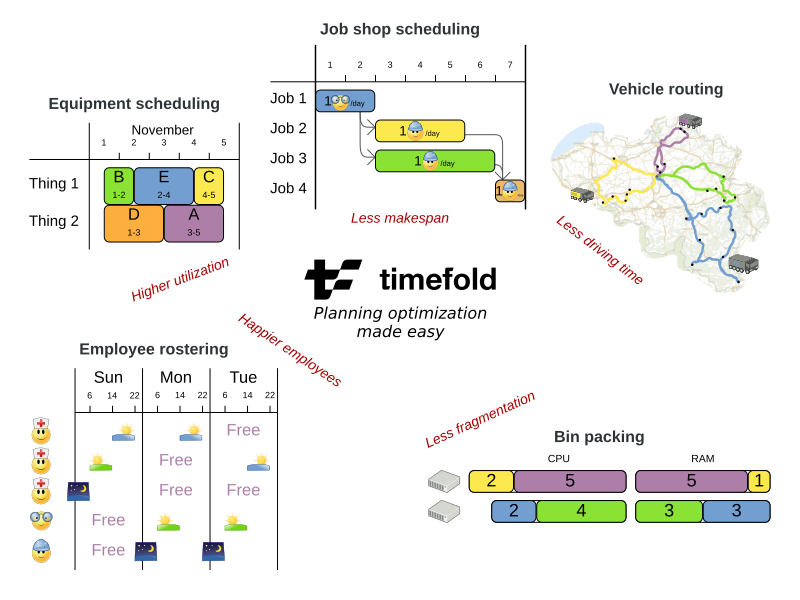
2. What is a planning problem?

A planning problem has an optimal goal, based on limited resources and under specific constraints. Optimal goals can be any number of things, such as:
-
Maximized profits - the optimal goal results in the highest possible profit.
-
Minimized ecological footprint - the optimal goal has the least amount of environmental impact.
-
Maximized satisfaction for employees or customers - the optimal goal prioritizes the needs of employees or customers.
The ability to achieve these goals relies on the number of resources available, such as:
-
The number of people.
-
Amount of time.
-
Budget.
-
Physical assets, for example, machinery, vehicles, computers, buildings, etc.
Specific constraints related to these resources must also be taken into account, such as the number of hours a person works, their ability to use certain machines, or compatibility between pieces of equipment.
Timefold Solver helps JavaTM, Kotlin and Python programmers solve constraint satisfaction problems efficiently. Under the hood, it combines optimization heuristics and metaheuristics with very efficient score calculation.
2.1. A planning problem is NP-complete or NP-hard
All the use cases above are probably NP-complete/NP-hard, which means in layman’s terms:
-
It’s easy to verify a given solution to a problem in reasonable time.
-
There is no silver bullet to find the optimal solution of a problem in reasonable time (*).
|
(*) At least, none of the smartest computer scientists in the world have found such a silver bullet yet. But if they find one for 1 NP-complete problem, it will work for every NP-complete problem. In fact, there’s a $ 1,000,000 reward for anyone that proves if such a silver bullet actually exists or not. |
The implication of this is pretty dire: solving your problem is probably harder than you anticipated, because the two common techniques won’t suffice:
-
A Brute Force algorithm (even a smarter variant) will take too long.
-
A quick algorithm, such as in bin packing, putting in the largest items first, will return a solution that is far from optimal.
By using advanced optimization algorithms, Timefold Solver does find a near-optimal solution in reasonable time for such planning problems.
2.2. A planning problem has (hard and soft) constraints
Usually, a planning problem has at least two levels of constraints:
-
A (negative) hard constraint must not be broken. For example: 1 teacher cannot teach 2 different lessons at the same time.
-
A (negative) soft constraint should not be broken if it can be avoided. For example: Teacher A does not like to teach on Friday afternoon.
Some problems have positive constraints too:
-
A positive soft constraint (or reward) should be fulfilled if possible. For example: Teacher B likes to teach on Monday morning.
Some basic problems only have hard constraints. Some problems have three or more levels of constraints - hard, medium and soft constraints.
These constraints define the score calculation (AKA fitness function) of a planning problem. Each solution of a planning problem can be graded with a score. With Timefold Solver, problems are modeled in an object-oriented paradigm in languages such as JavaTM, Kotlin or Python.. Such code is easy, flexible and scalable.
2.3. A planning problem has a huge search space
A planning problem has a number of solutions. There are several categories of solutions:
-
A possible solution is any solution, whether or not it breaks any number of constraints. Planning problems tend to have an incredibly large number of possible solutions. Many of those solutions are worthless.
-
A feasible solution is a solution that does not break any (negative) hard constraints. The number of feasible solutions tends to be relative to the number of possible solutions. Sometimes there are no feasible solutions. Every feasible solution is a possible solution.
-
An optimal solution is a solution with the highest score. Planning problems tend to have 1 or a few optimal solutions. There is always at least 1 optimal solution, even in the case that there are no feasible solutions and the optimal solution isn’t feasible.
-
The best solution found is the solution with the highest score found by an implementation in a given amount of time. The best solution found is likely to be feasible and, given enough time, it’s an optimal solution.
Counterintuitively, the number of possible solutions is huge (if calculated correctly), even with a small dataset. As you can see in the examples, most instances have a lot more possible solutions than the minimal number of atoms in the known universe (10^80). Because there is no silver bullet to find the optimal solution, any implementation is forced to evaluate at least a subset of all those possible solutions.
Timefold Solver supports several optimization algorithms to efficiently wade through that incredibly large number of possible solutions. Depending on the use case, some optimization algorithms perform better than others, but it’s impossible to tell in advance. With Timefold Solver, it is easy to switch the optimization algorithm, by changing the solver configuration in a few lines of code.
3. Status of Timefold Solver
Timefold Solver is 100% pure JavaTM and runs on Java 17 or higher. It integrates very easily with other JavaTM technologies. Timefold Solver works on any Java Virtual Machine and is compatible with the major JVM languages and all major platforms. It also supports Kotlin and Python.
Timefold Solver is stable, reliable and scalable. It has been heavily tested with unit, integration, and stress tests, and is used in production throughout the world. One example handles over 50 000 variables with 5000 values each, multiple constraint types and billions of possible constraint matches.
We offer two editions of Timefold Solver.
3.1. Timefold Solver Community Edition
Timefold Solver Community Edition is open source software, released under the Apache License 2.0. This license is very liberal and allows reuse for commercial purposes. Read the layman’s explanation.
Timefold Solver Community Edition is available in the Maven Central Repository. It is and will always be free. The overwhelming majority of solver features will always be available in the Community Edition. Most users will be able to solve their planning problems with the Community Edition.
3.2. Timefold Solver Enterprise Edition
Timefold Solver Enterprise Edition is a commercial product that offers additional features to scale out to very large datasets. To find out more, see Enterprise Edition section of this documentation.
4. Backwards compatibility
Timefold Solver separates its API from its implementation:
-
Public API: All classes in the following package namespaces are 100% backwards compatible in future releases, especially minor and hotfix releases:
-
ai.timefold.solver.core.api -
ai.timefold.solver.benchmark.api -
ai.timefold.solver.test.api -
ai.timefold.solver…api*
-
-
Configuration: The solver configuration is backwards compatible for all elements, except for elements that require the use of non-public API classes. The solver configuration is defined by the classes in the following package namespaces:
-
ai.timefold.solver.core.config -
ai.timefold.solver.benchmark.config
-
-
Implementation classes: All other classes are not backwards compatible. They will change in future major or minor releases, but probably not in hotfix releases.
Backwards incompatible changes will be clearly documented in the upgrade recipe.
|
This documentation covers some |
5. Start using Timefold Solver
5.1. Use Timefold Solver with Maven or Gradle
The Timefold Solver jars are available in the central maven repository.
-
Maven
-
Gradle
Add a dependency to timefold-solver-core in your pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-core</artifactId>
<version>...</version>
</dependency>Or better yet, import the timefold-solver-bom in dependencyManagement to avoid duplicating version numbers
when adding other timefold dependencies later on:
<project>
...
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-bom</artifactId>
<type>pom</type>
<version>...</version>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
</project>Add a dependency to timefold-solver-core in your build.gradle:
dependencies {
implementation 'ai.timefold.solver:timefold-solver-core:...'
}See also how to switch To Enterprise Edition.
To find out how to get started with Timefold Solver, see Quickstarts.
5.2. Upgrade to the latest version
See the dedicated section on Upgrade and Migration.