Model the domain objects
Your goal is to assign each visit to a vehicle. You will create these classes:
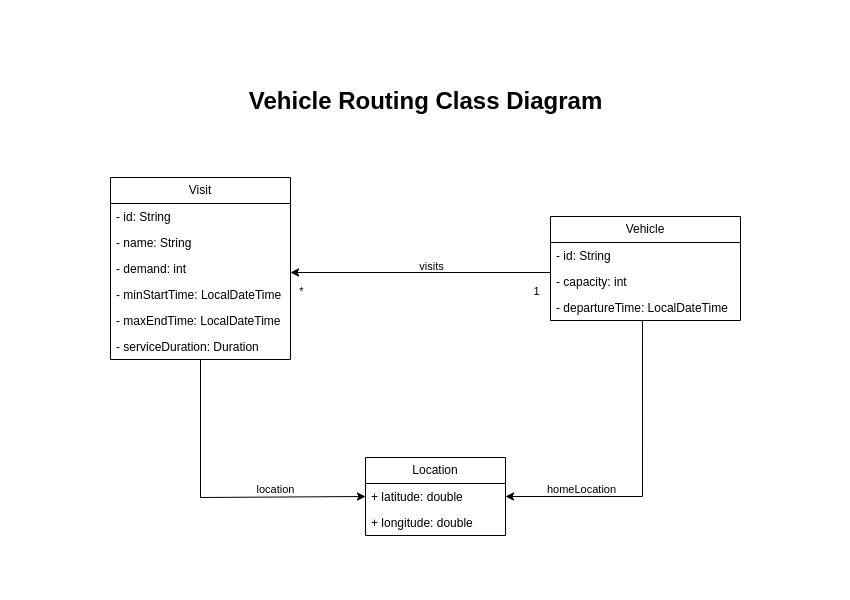
Location
The Location class is used to represent the destination for deliveries or the home location for vehicles.
The drivingTimeSeconds map contains the time required to drive from this location to any other location.
This field will be initialized later.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Location.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain;
import java.util.Map;
public class Location {
private double latitude;
private double longitude;
private Map<Location, Long> drivingTimeSeconds;
public Location(double latitude, double longitude) {
this.latitude = latitude;
this.longitude = longitude;
}
public double getLatitude() {
return latitude;
}
public double getLongitude() {
return longitude;
}
public Map<Location, Long> getDrivingTimeSeconds() {
return drivingTimeSeconds;
}
public void setDrivingTimeSeconds(Map<Location, Long> drivingTimeSeconds) {
this.drivingTimeSeconds = drivingTimeSeconds;
}
public long getDrivingTimeTo(Location location) {
return drivingTimeSeconds.get(location);
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Location.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain
class Location @JsonCreator constructor(val latitude: Double, val longitude: Double) {
var drivingTimeSeconds: Map<Location, Long>? = null
fun getDrivingTimeTo(location: Location): Long {
if (drivingTimeSeconds == null) {
return 0
}
return drivingTimeSeconds!![location]!!
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "$latitude,$longitude"
}
}Vehicle
Vehicle has a defined route plan with scheduled visits to make.
Each vehicle has a specific departure time and starting location.
It returns to its home location after completing the route and has a maximum capacity that must not be exceeded.
During solving, Timefold Solver updates the visits field of the Vehicle class to assign a list of visits.
Because Timefold Solver changes this field, Vehicle is a planning entity:
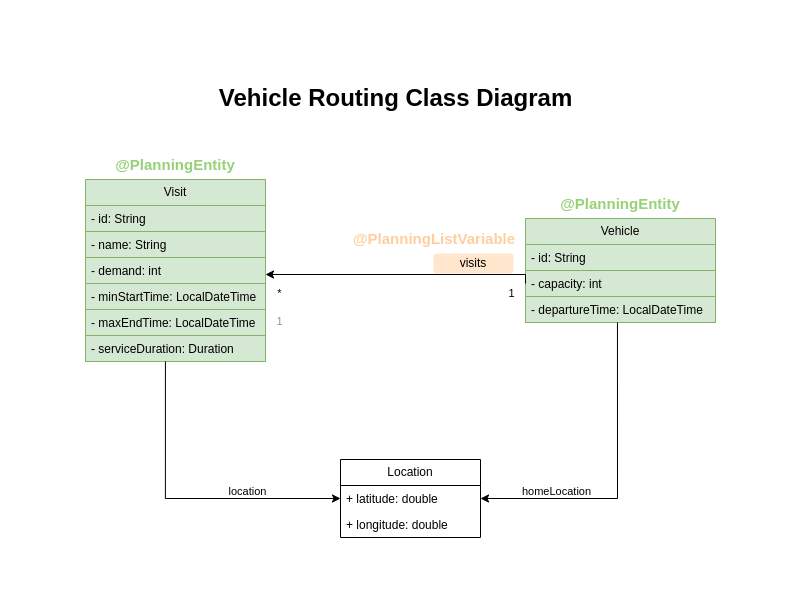
Based on the diagram, the visits field is a genuine variable that changes during the solving process.
To ensure that Timefold Solver recognizes it as a sequence of connected variables,
the field must have an @PlanningListVariable annotation indicating that the solver can distribute a subset of the
available visits to it.
The objective is to create an ordered scheduled visit plan for each vehicle.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Vehicle.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.entity.PlanningEntity;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.lookup.PlanningId;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.PlanningListVariable;
@PlanningEntity
public class Vehicle {
@PlanningId
private String id;
private int capacity;
private Location homeLocation;
private LocalDateTime departureTime;
@PlanningListVariable
private List<Visit> visits;
public Vehicle() {
}
public Vehicle(String id, int capacity, Location homeLocation, LocalDateTime departureTime) {
this.id = id;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.homeLocation = homeLocation;
this.departureTime = departureTime;
this.visits = new ArrayList<>();
}
// Getters and Setters excluded
public int getTotalDemand() {
int totalDemand = 0;
for (Visit visit : visits) {
totalDemand += visit.getDemand();
}
return totalDemand;
}
public long getTotalDrivingTimeSeconds() {
if (visits.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
long totalDrivingTime = 0;
Location previousLocation = homeLocation;
for (Visit visit : visits) {
totalDrivingTime += previousLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(visit.getLocation());
previousLocation = visit.getLocation();
}
totalDrivingTime += previousLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(homeLocation);
return totalDrivingTime;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id;
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Vehicle.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain
import java.time.LocalDateTime
import java.util.ArrayList
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.entity.PlanningEntity
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.lookup.PlanningId
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.PlanningListVariable
@PlanningEntity
class Vehicle {
@PlanningId
lateinit var id: String
var capacity: Int = 0
lateinit var homeLocation: Location
lateinit var departureTime: LocalDateTime
@PlanningListVariable
var visits: List<Visit>? = null
constructor()
constructor(id: String, capacity: Int, homeLocation: Location, departureTime: LocalDateTime) {
this.id = id
this.capacity = capacity
this.homeLocation = homeLocation
this.departureTime = departureTime
this.visits = ArrayList()
}
val totalDemand: Long
get() {
var totalDemand = 0L
for (visit in visits!!) {
totalDemand += visit.demand
}
return totalDemand
}
val totalDrivingTimeSeconds: Long
get() {
if (visits!!.isEmpty()) {
return 0
}
var totalDrivingTime: Long = 0
var previousLocation = homeLocation
for (visit in visits!!) {
totalDrivingTime += previousLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(visit.location!!)
previousLocation = visit.location!!
}
totalDrivingTime += previousLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(homeLocation)
return totalDrivingTime
}
override fun toString(): String {
return id
}
}The Vehicle class has an @PlanningEntity annotation,
so Timefold Solver knows that this class changes during solving because it contains one or more planning variables.
Notice the toString() method keeps the output short,
so it is easier to read Timefold Solver’s DEBUG or TRACE log, as shown later.
|
Determining the |
Visit
The Visit class represents a delivery that needs to be made by vehicles.
A visit includes a destination location, a delivery time window represented by [minStartTime, maxEndTime],
a demand that needs to be fulfilled by the vehicle, and a service duration time.
The Visit class has an @PlanningEntity annotation
but no genuine variables and is called a shadow entity.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
Create or adjust the src/main/java/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Visit.java class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.entity.PlanningEntity;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.lookup.PlanningId;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.InverseRelationShadowVariable;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.NextElementShadowVariable;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.PreviousElementShadowVariable;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.ShadowVariable;
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.solver.ArrivalTimeUpdatingVariableListener;
@PlanningEntity
public class Visit {
@PlanningId
private String id;
private String name;
private Location location;
private int demand;
private LocalDateTime minStartTime;
private LocalDateTime maxEndTime;
private Duration serviceDuration;
@InverseRelationShadowVariable(sourceVariableName = "visits")
private Vehicle vehicle;
@PreviousElementShadowVariable(sourceVariableName = "visits")
private Visit previousVisit;
@CascadingUpdateShadowVariable(targetMethodName = "updateArrivalTime")
private LocalDateTime arrivalTime;
public Visit() {
}
public Visit(String id, String name, Location location, int demand,
LocalDateTime minStartTime, LocalDateTime maxEndTime, Duration serviceDuration) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.location = location;
this.demand = demand;
this.minStartTime = minStartTime;
this.maxEndTime = maxEndTime;
this.serviceDuration = serviceDuration;
}
// Getters and Setters excluded
private void updateArrivalTime() {
if (previousVisit == null && vehicle == null) {
arrivalTime = null;
return;
}
LocalDateTime departureTime = previousVisit == null ? vehicle.getDepartureTime() : previousVisit.getDepartureTime();
arrivalTime = departureTime != null ? departureTime.plusSeconds(getDrivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill()) : null;
}
public LocalDateTime getDepartureTime() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return null;
}
return getStartServiceTime().plus(serviceDuration);
}
public LocalDateTime getStartServiceTime() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return null;
}
return arrivalTime.isBefore(minStartTime) ? minStartTime : arrivalTime;
}
public boolean isServiceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime() {
return arrivalTime != null
&& arrivalTime.plus(serviceDuration).isAfter(maxEndTime);
}
public long getServiceFinishedDelayInMinutes() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return 0;
}
return Duration.between(maxEndTime, arrivalTime.plus(serviceDuration)).toMinutes();
}
public long getDrivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill() {
if (vehicle == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"This method must not be called when the shadow variables are not initialized yet.");
}
if (previousVisit == null) {
return vehicle.getHomeLocation().getDrivingTimeTo(location);
}
return previousVisit.getLocation().getDrivingTimeTo(location);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id;
}
}Create the src/main/kotlin/org/acme/vehiclerouting/domain/Visit.kt class:
package org.acme.vehiclerouting.domain
import java.time.Duration
import java.time.LocalDateTime
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.entity.PlanningEntity
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.lookup.PlanningId
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.InverseRelationShadowVariable
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.NextElementShadowVariable
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.PreviousElementShadowVariable
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.domain.variable.ShadowVariable
import org.acme.vehiclerouting.solver.ArrivalTimeUpdatingVariableListener
@PlanningEntity
class Visit {
@PlanningId
lateinit var id: String
lateinit var name: String
lateinit var location: Location
var demand: Int = 0
lateinit var minStartTime: LocalDateTime
lateinit var maxEndTime: LocalDateTime
lateinit var serviceDuration: Duration
@InverseRelationShadowVariable(sourceVariableName = "visits")
private var vehicle: Vehicle? = null
@PreviousElementShadowVariable(sourceVariableName = "visits")
var previousVisit: Visit? = null
@CascadingUpdateShadowVariable(targetMethodName = "updateArrivalTime")
var arrivalTime: LocalDateTime? = null
constructor()
constructor(
id: String, name: String, location: Location, demand: Int,
minStartTime: LocalDateTime, maxEndTime: LocalDateTime, serviceDuration: Duration
) {
this.id = id
this.name = name
this.location = location
this.demand = demand
this.minStartTime = minStartTime
this.maxEndTime = maxEndTime
this.serviceDuration = serviceDuration
}
private fun updateArrivalTime() {
if (previousVisit == null && vehicle == null) {
arrivalTime = null
return
}
val departureTime = previousVisit?.departureTime ?: vehicle?.departureTime
arrivalTime = departureTime?.plusSeconds(getDrivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill())
}
val departureTime: LocalDateTime?
get() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return null
}
return startServiceTime!!.plus(serviceDuration)
}
val startServiceTime: LocalDateTime?
get() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return null
}
return if (arrivalTime!!.isBefore(minStartTime)) minStartTime else arrivalTime
}
val isServiceFinishedAfterMaxEndTime: Boolean
get() = (arrivalTime != null
&& arrivalTime!!.plus(serviceDuration).isAfter(maxEndTime))
val serviceFinishedDelayInMinutes: Long
get() {
if (arrivalTime == null) {
return 0
}
return Duration.between(maxEndTime, arrivalTime!!.plus(serviceDuration)).toMinutes()
}
val drivingTimeSecondsFromPreviousStandstill: Long
get() {
if (vehicle == null) {
throw IllegalStateException(
"This method must not be called when the shadow variables are not initialized yet."
)
}
if (previousVisit == null) {
return vehicle!!.homeLocation.getDrivingTimeTo(location)
}
return previousVisit!!.location.getDrivingTimeTo((location))
}
override fun toString(): String {
return id
}
}Some methods are annotated with @InverseRelationShadowVariable, @PreviousElementShadowVariable and @CascadingUpdateShadowVariable.
They are called shadow variables,
and because Timefold Solver changes them,
Visit is a planning entity:
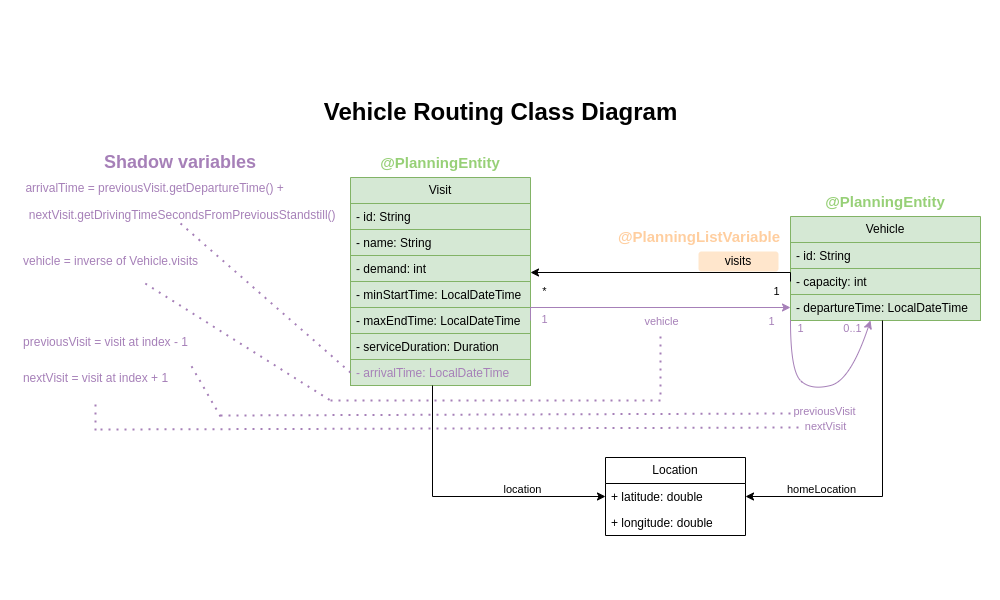
The field vehicle has an @InverseRelationShadowVariable annotation,
creating a bi-directional relationship with the Vehicle.
The function returns a reference to the Vehicle where the visit is scheduled.
Let’s say the visit Ann was scheduled to the vehicle V1 during the solving process.
The method returns a reference of V1.
The field previousVisit is annotated with @PreviousElementShadowVariable.
The solver will update this field with a reference of the visit preceding the current visit instance.
Assuming that vehicle V1 is assigned the visits of Ann, Beth, and Carl,
the previousVisit field will be filled with Ann for the visit of Beth.
@NextElementShadowVariable also exists, which can be used to get a reference to the successor element.
|
The arrivalTime field has a @CascadingUpdateShadowVariable annotation.
This annotation indicates which method should be triggered to update this field whenever this entity is moved, in this case the updateArrivalTime() method.
This change is automatically propagated to the subsequent visits and stops when the arrivalTime value hasn’t changed or when it’s reached the end of the chain of visit objects.