Real-time planning with /from-patch (preview)
|
This guide describes functionality that is currently available as a preview feature. If you’d like early access to this feature, please Contact us. |
Benefits of patching a dataset instead of rebuilding
By default, the Timefold platform follows a run-based model: every time you want to solve a planning problem, you send the full dataset and get back the results. This works well for many use cases, but it becomes cumbersome when:
-
You want to make small changes (e.g. update one employee’s availability, pin a specific shift, or add an extra visit).
-
You want to use results from a previous optimization (e.g. to minimize disruption).
When always starting from scratch, you have to rebuild and resend the entire dataset, merge results from previous datasets into new input, and work without traceability between datasets.
The /from-patch endpoint on a dataset makes replanning smoother. Instead of resending the full dataset, you work
with an existing dataset and apply small, targeted patches:
-
Apply incremental changes, such as “add this task” or “remove this employee”.
-
Safely experiment: each patch creates a new dataset.
-
Keep traceability: track how a plan evolved over time, roll back to earlier datasets, and analyze the impact of each change.
This shift (from runs to datasets and operations) reduces API overhead and makes it easier to collaborate on evolving plans.
Concepts of the /from-patch endpoint
-
Existing dataset as a base
You call/from-patchon an existing dataset. The result is a new dataset that contains your changes, with the original dataset tracked as its parent. -
Control over re-optimization
When submitting a patch, you can decide whether or not the system should re-optimize immediately after applying the change. (Via theoperationparameter.) -
Start from solved or unsolved data (Via the
selectparameter)
You can apply patches either to:-
The solved dataset (preserving current assignments, useful if the model supports replanning with minimizing disruption).
-
The unsolved dataset (discarding previous assignments and treating it as a fresh planning problem).
-
-
Operations work on the modelInput
The supplied patches operate on themodelInputfor the base. Additionally, you can submit updated configuration or configuration profiles.
See API usage to learn about how to explore the OpenAPI specifications for the /from-patch endpoint of Timefold Models.
Patch payload format
The /from-patch endpoint accepts a JSON payload inspired by the JSON Patch standard, defined in RFC 6902.
This RFC specifies a format for describing changes to a JSON document using a sequence of operations. These operations are applied in order to transform the target document into the desired state.
A single patch operation looks like:
{
"op": "<operation>",
"path": "<path>",
"value": <optional-value>
}Our implementation however, has a few key differences:
-
Supported operations: add, remove, replace.
-
Extended path syntax: you can select array items not only by index, but by filtering on a property value.
-
Equality comparisons only.
-
Single-attribute selection only.
-
Example paths:
-
/employees/[id=Lee]/tags→ targets the tags field for the employee with id Lee. -
/vehicles/[id=Ann Cole]/shifts/[id=cd4c29ed]/skills→ targets the skills of a specific shift within a specific vehicle. -
/vehicles/-→ targets a new item in the vehicles array.
Examples
Here are a few examples to demonstrate the functionality.
The exact values for path and value will depend on the schema of the modelInput for the model.
Add a new employee
[
{
"op": "add",
"path": "/employees/-",
"value": {
"id": "Ann Cole",
"skills": [{ "id": "Ambulance" }]
}
}
]Multiple operations, validation, and traceability
Multiple operations
-
You can submit several patch operations in one request.
-
Operations are executed in the order they appear.
-
Each operation works on the result of the previous one, so you can chain changes.
Validation
For speed, validation happens only after all operations have been applied. (If validation fails, there is no direct link to the specific operation that caused the issue.)
There are two validation steps:
-
JSON Schema validation: When submitting the patch, the updated dataset is validated against the JSON schema. If errors occur here because the JSON is not valid, the dataset will not be created, and the API will return an error.
-
Model validation: Once created, the dataset is also validated by the model itself (e.g. checking required skills or more complex domain-specific rules). If this fails, the dataset enters the state
DATASET_INVALID. See Dataset lifecycle for details.
Traceability in the UI
The Timefold Platform UI makes it easy to understand the lineage and history of datasets.
-
On the Dataset detail pages:
-
The sidebar displays Parent dataset ID and the Origin dataset ID, so you can easily track the revisions of a dataset and identify the original dataset.
-
A dropdown lets you switch between revisions of the same plan.
-
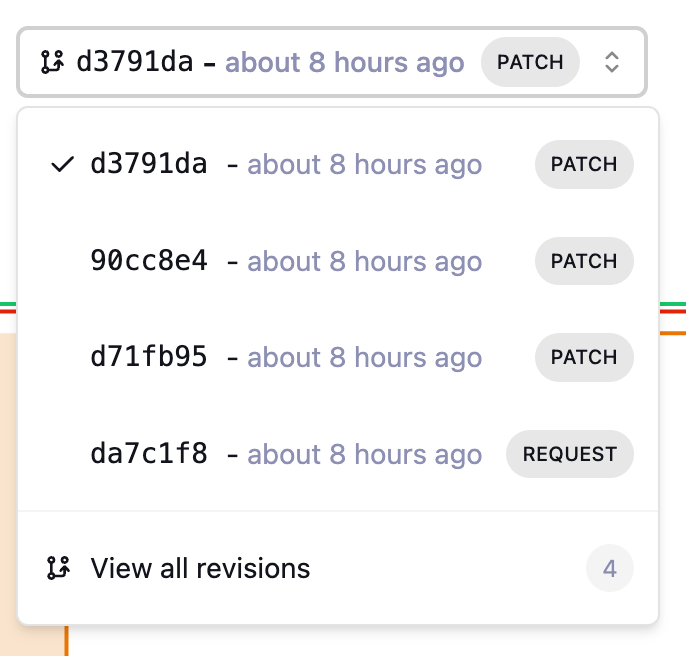
-
On the Dataset’s Input page:
-
You can see and download both the JSON patch request and the resulting dataset input.
-
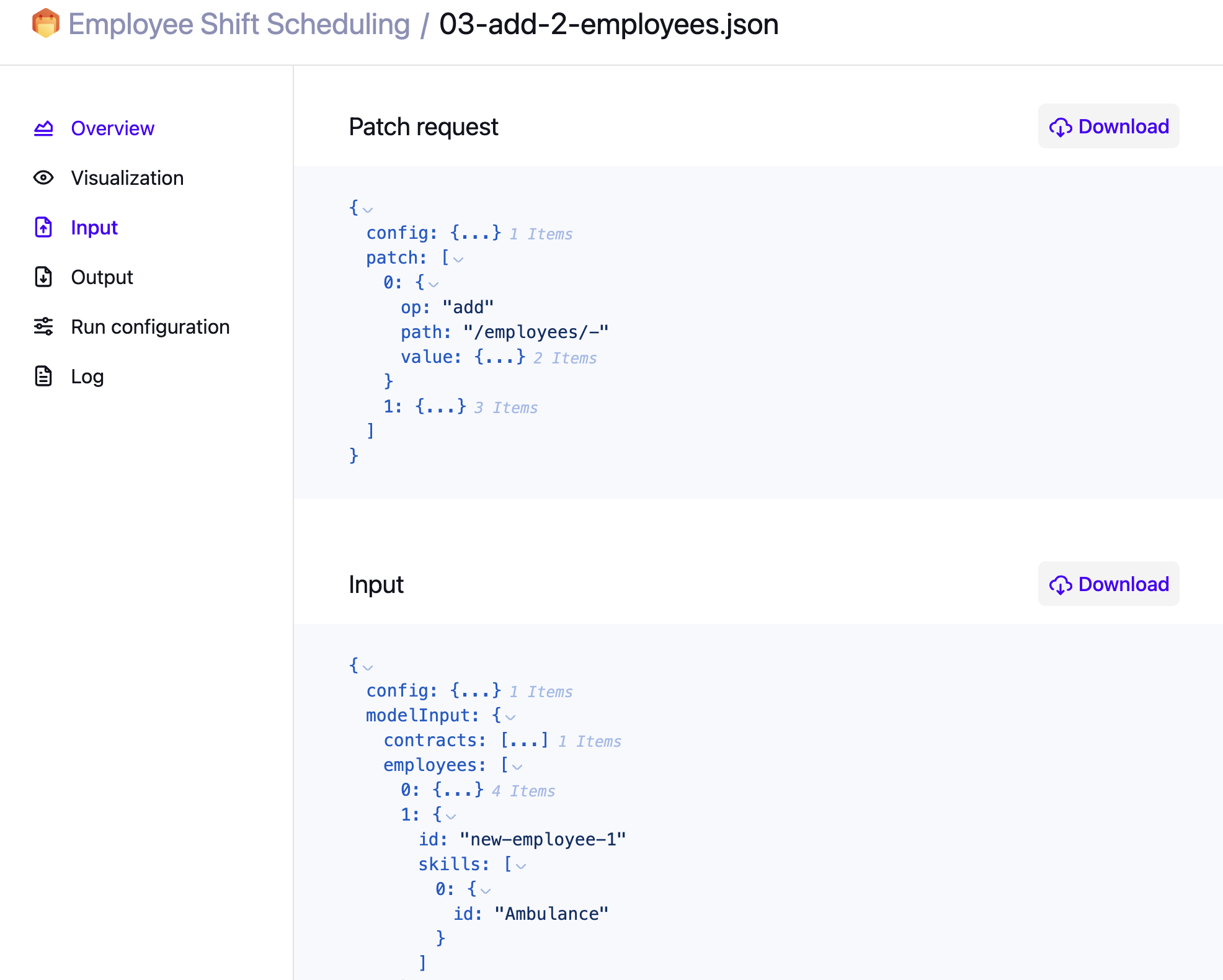
-
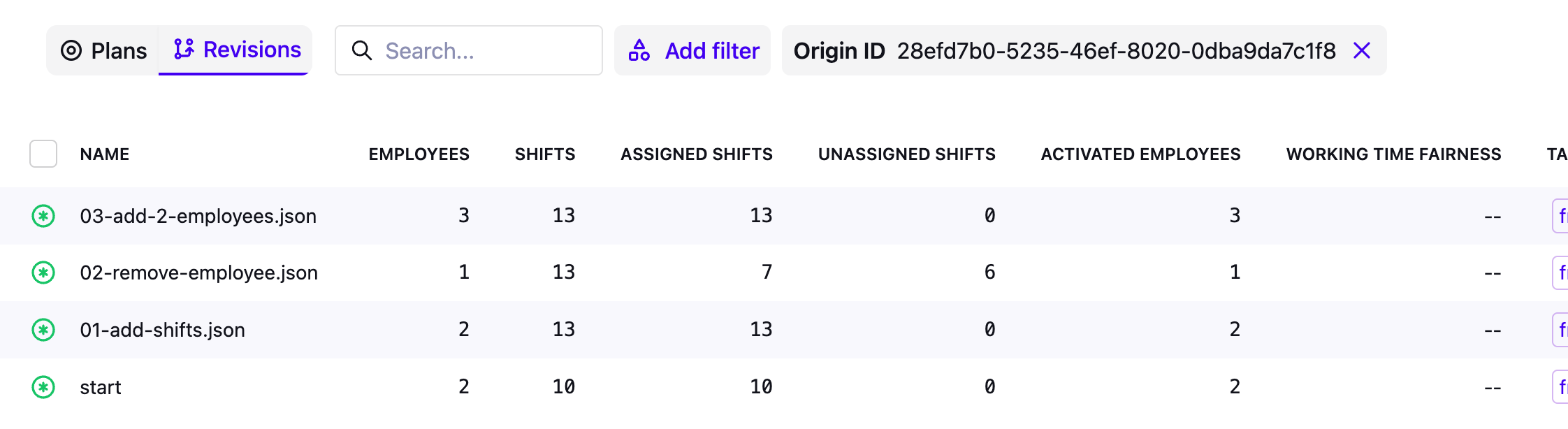
On the Plans overview page:
-
You can use the toggle to switch between showing only original plans and all revisions, including datasets created from patches.
-
You can filter by the “Origin ID” field to see all datasets/revisions that originated from the given original plan.
-
You can filter by the “Created from” field to see all datasets that originated from a patch.
-
Tips for patching
While patching has benefits, there are a few important considerations:
-
Auditability is key
When you send a patch, you assume that it makes the intended changes. This is why the UI shows both the submitted patch and the resulting input dataset. Especially during development, always verify that patches behave as expected. -
Source of truth
We recommend not using Timefold as the source of truth for your business data, except for the assignments themselves. The patch endpoint makes it easier to send incremental changes (including from different systems), but your own systems should remain the authoritative source for input data. -
Verification
You can fetch the updated dataset’s input after a patch is applied and compare it against your internal state to ensure consistency. -
Complementary, not a replacement
The patch endpoint does not replace any existing API calls. As an API user, you can always decide whether it’s better to apply a patch or to rebuild and submit a full dataset from scratch.
Coupled datasets
Every dataset created with /from-patch keeps a link to its parent dataset. This means you can:
-
Track the full history of a plan across changes.
-
Roll back to earlier datasets when needed.
-
Compare metrics and score analysis between datasets to see the effect of disruptions and changes. See Comparing datasets (preview) for details.
This creates a natural versioning system for real-time plans.
Preview status
|
The This also means:
|
For a deeper dive into the challenges of real-time planning, see our guide: Responding to disruptions with real-time planning